About Mapper2d
The Mapper2d allows to define and preview content mapping on a screen.
The Mapper2d bases its calculations on measurements of the projectionsystem. The measurements are done with Creator or Align.
It can export the resulting correction data for several presentation systems, warping software and warping hardware.
Main window overview
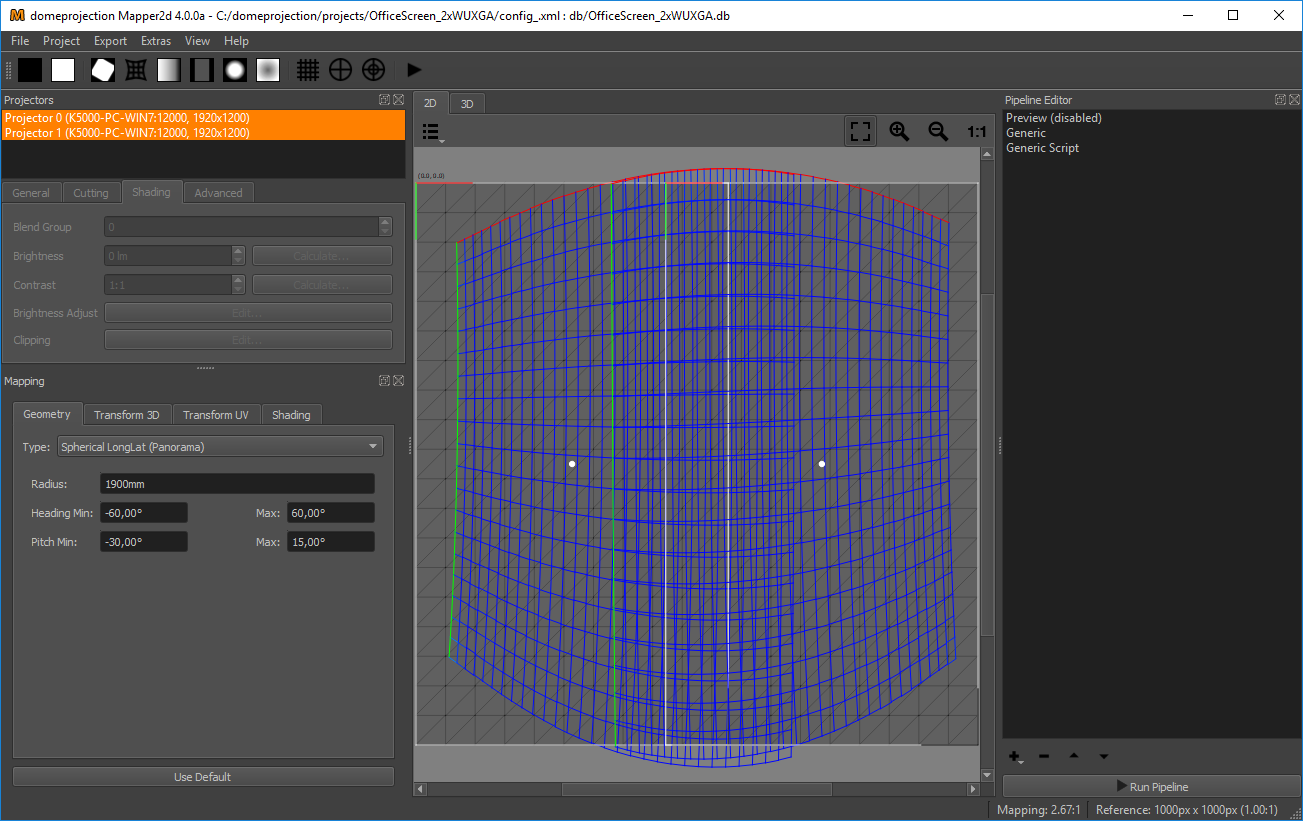
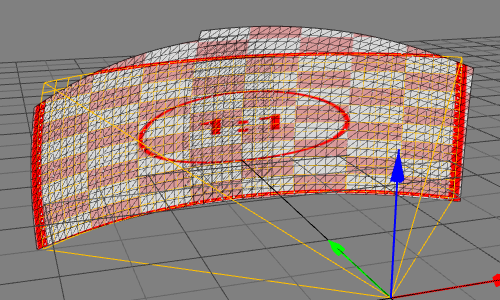
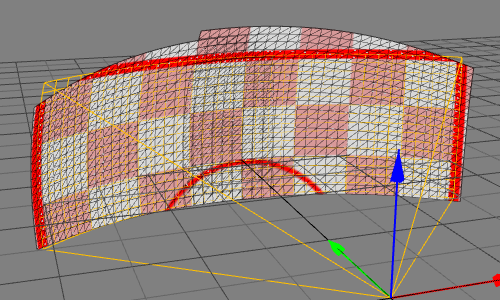
Mapper2d main window
Mapper2d has a fully configurable workspace. Above figure shows the default configuration with the typical widgets open.
- Menus
- File Menu
Load and save projects. Adjust global project settings.
- Export Menu
Export calibration data from current project using available exporters. Please refer to section Exporters for a list of all available exporters.
Export settings used here are non-persistent. This is useful for experimenting with different settings, without changing a previously defined autoalignment work-flow for instance. Section Pipeline Editor describes how to save persistent export settings using the Pipeline Editor.
- Extras Menu
Additional tools and advanced operations on loaded project.
- View Menu
Workspace and theme management.
- Help Menu
Help, Support and Program information.
- Toolbar
The toolbar provides quick access to several previews (see Preview Toolbar) and an automization run.
- Docks
Here a list of the most important docks, also shown in the screen shot.
- Projector List
The projectors dock widget shows a list of all projectors in the current project and allows to edit projector related settings.
- Mapping
2D mapping of the projection, used for applying clipping, fadeout and calculating blending.
- Pipeline Editor
On the right side in the Pipeline Editor exporters can be configured with persistent settings to run multiple times.
- Central Views
In the center of the window are multiple views available between which the user can switch.
- Statusbar
Gives information about aspect ratio of currently setup mapping.
All dock widgets can be arranged, stacked, opened and closed by user. The workspace layout is saved persistently.
It is also possible to revert to the default workspace using View/Default Workspace.
All available dock widgets can be found in the menu. They are described in the following sections.
The theme can be switched in View/Theme. An application restart is needed for a
theme switch to take effect.
For using the maximum workspace on the desktop, a full screen mode can
be enabled in View/Toggle Fullscreen Mode.
Projector List
There are different kinds of information stored for each projector. All projector related values are managed by the tabs below the projector list, which apply to the selected projectors.
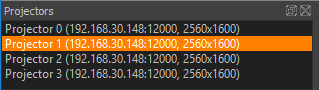
Projector List
The list shows the given Projector name, its IP address with port, the resolution and if an alignment is available (aligned).
The projector list is multi-selection enabled. Only selected projectors
are shown in the 2d- and 3d-view. Press Ctrl-A to select all
projectors at once or hold Ctrl- or Shift-key to add projectors to
current selection.
Projector settings can be edited when a single projector is selected, otherwise the projector settings placed below the projector list are grayed out.
General Settings
The general settings, reflect the physical setup. Usually all data here is filled out in advance through the calibration setup. Changes here should only be done when the physical setup has changed (for example due to network reconfiguration, computer replacement, or rewiring)
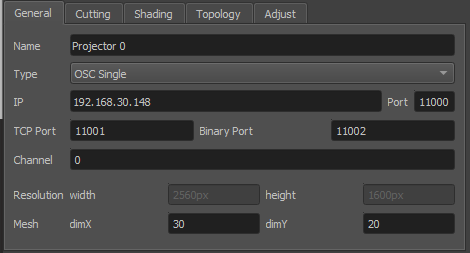
General Settings
- Name
Human readable string describing the projector.
- Type
Interface to use for showing testpatterns.
- OSC Single
Default PatternGenerator based interface. Works with up to date PatternGenerator.
- OSC Multi
ProjectionTools channels are virtually split into multiple PatternGenerator channels. Works with standard PatternGenerator.
- OSC Legacy
Can be used for very old PatternGenerator installations, or installations on limited/embedded hardware. The preview functionality is limited.
- NDI
Provide testpatterns as one NDI-stream per channel. This can be used, if it is not possible to install PatternGenerator on the Mediaservers. Several Mediaservers support recieving and showing NDI-Streams. The preview functionality is limited.
- Norxe Unify
Send testpatterns as image directly to Norxe Unify projectors. This allows calibration without access to IGs.The preview functionality is limited, and not interactive.
- Barco Pulse
Send testpatterns as image directly to Barco Pulse projectors. This allows calibration without access to IGs.The preview functionality is limited, and not interactive.
- Luna
Send testpatterns as image directly to domeprojection Luna warp units. This allows calibration without access to IGs.The preview functionality is limited, and not interactive.
- Warper4k
Send testpatterns as image directly to Westar Warper4k warp units. This allows calibration without access to IGs.The preview functionality is limited, and not interactive.
- IP
Network address of computer where PatternGenerator software is running on. Hostnames are supported as well.
- Port
Networkport to communicate with PatternGenerator. By default 11000
- Channel
The Channel is used to address a projector if more than one is connected to a single PC
- Width and height
Have to be the same as the physical projector resolution used in the projection and displayed here for reference only (not editable).
- dim X and dim Y
Attribute, defining the resolution of the warping grid. Larger values may gain better results but some constraints apply. There are hard limits depending on the warping unit. Bigger values are increasing the calculation time of many operations significantly, especially
Cutting
Cutting rectangles are auto generated by default. This way, they are automatically placed where the mapping of the projector is in the texture with some scale-factor (defined in project settings) increasing its size and auto rotated to best fit.
The auto generation can be disabled to allow user defined cutting rectangles (e.g. when they are already predetermined by projection design and content production). Another reason for disabling auto generation is when the cutting rectangles should no more change, e.g. when using pre-split video.
Cutting rectangles can also be placed in a regular grid with defined relative overlaps using:
Menu/Extras/Layout Cutting Rectangles
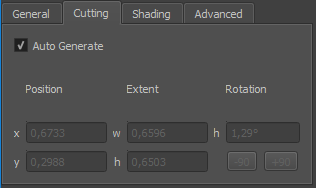
Cutting settings
- Auto Generate
Enable/Disable automatic generation and update of cutting rectangle. When disabled cutting rectangle settings can be edited by hand.
- Position X Y
Position of cutting rectangle center as normalized coordinate in texture space
- Extent W H
normalized width and height of cutting rectangle
- Rotation
Orientation of cutting rectangle as degrees clock-wise
- -90 / +90
Quickly spin cutting rectangle in 90 degree steps.
Spin cutting rectangles can be used to quickly fix auto generated cutting rectangles, whose orientation does not match the orientation of the projector mesh. For some warp units it is important that the cutting rectangle is aligned correctly, since the amount of warping that can be applied on these units is limited.
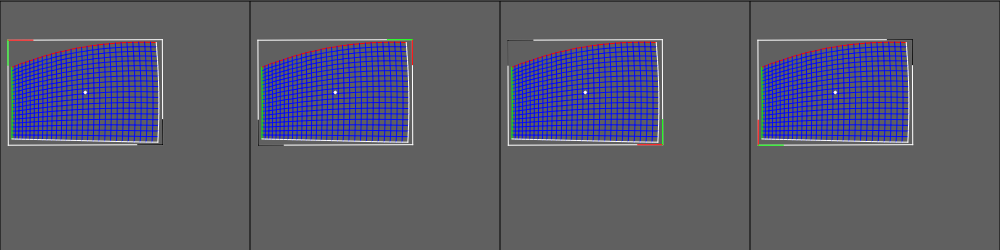
Cutting spin multiple times
Shading
The Shading panel expose blending properties which can be different for each projector. There are other values as well, which apply to the whole setup and are adjusted in different places.

Shading settings
- Blend Group
In order to increase light intensity, sometimes two projectors are used to project on the same area of the screen. This is a so called “tandem” or “stacked” projection. Since blending is typically calculated between all overlapping projectors, the brightness of the tandem projection pair would be reduced to the brightness of one projector canceling out the initial intention of the tandem projection. The proper use of Blend Groups helps in this case.
Blending is calculated between projectors of same blend group only. Use different blend groups for different layers of projection or projectors between which no blending should be calculated. The blend group element assigns a projector to a blend group. The default blend group is 0.
- Brightness
Brightness of projector in lumen. Used for uniformity correction calculations.
- Brightness Calculate
Allows to calculate projector brightness from measured brightness of projected image center and a given screen-gain. Shows a small white rectangle on the selected projector center for taking a measurement right away.
- Contrast
Contrast of projector, used for advanced black level correction calculations.
- Contrast Calculate
Allows to calculate projector contrast from black and white measured at center of projected image. Shows a black image and a small white image in projector center for taking measurements.
- Brightness Adjust
When global automatic uniformity correction is disabled, it allows to edit custom uniformity correction for a projector. See section Uniformity Correction Editor for details.
- Clipping
Allows to clip parts of the current projector. The clipped parts will be covered by neighboring projectors if present. It is usually used, if projectors are partly shadowed by obstacles.
Topology
Relation between channels.
- Touching Channels
Define the neighboring channels for high resolution projectors (see section Touching Channels).
- Mapping
When a project has multiple mappings defined, this setting is available and allows to assign a channel to a mapping (see section Multiple Mappings).
Adjust
Allows to do additional, manual adjustment of geometry and color uniformity.
- Shading
Adjust brightness and color up to pixel level.
- Brightness Adjust
When global automatic uniformity correction is disabled, it allows to edit custom uniformity correction for a projector. See section Uniformity Correction Editor for details.
- Clipping
Allows to clip parts of the current projector. The clipped parts will be covered by neighboring projectors if present. It is usually used, if projectors are partly shadowed by obstacles.
- WhitePoint
Allows to adjust the color uniformity of a projector. This correction is combined with the standard uniformity correction of a projector.
Please be aware, that color uniformity correction is not compatible with all systems.
- Init Preview
Uploads blending information to the PatternGenerator, so that an interactive preview can be shown while editing the whitepoint color uniformity.
- Reset Preview
Puts PatternGenerator in a clean state again, compatible with standard previews.
- Edit
Opens an Uniformity Correction Editor (see section Uniformity Correction Editor), with color editing enabled.
- Blanking
If a projector has poor projection quality at the edges or corners, these areas can be removed using the blanking option. Adjust the amount of blanking for left, right, top, bottom edge and preview the results using the “Preview Cutting”. This feature does not change the resulting warping. The blanking is encoded in the exported blending as black areas.
- Black Level Correction
Control appearance of projection when dark/black content is projected.
- Uniformity
Allows to change the color of the software black level correction. This is sometimes necessary, if the native black of a projector has a different color than the lower gray levels. It is suggested to turn “Advanced BLC” off in project settings and set a relative high “Black Level”, in order to have a good starting point.
It is also possible to adjust multiple projectors at once by selecting the relevant projectors in the projector list and using
Extras/BLC Tweak Initialize...followed byExtras/Tweak Black Level Correction....Note
Please be aware, that colored black level correction is not compatible with all systems.
- Init Preview
Prepares the PatternGenerator to show an interactive preview while editing the black level color uniformity.
- Reset Preview
Puts PatternGenerator in a clean state again, compatible with standard previews.
- Edit
Opens an Uniformity Correction Editor (see section Uniformity Correction Editor), with color editing enabled.
- Override Chip Oversize
Overrides the globally set Chip Oversize per projector (see section Shading).
- Geometry
Allows to slightly adjust the warping. It is rarely used to handle errors or unusual setups, which are not covered by standard attributes. Please note, these parameters affect the calculations directly and may have unexpected side effects. The adjustment values will shift the calculated warping by factor*value. Its main use is like shifting a projector manually.
Note
Those properties should be used to adjust the projection manually instead of modifying it on the output device, because changes here will be exported after each autoalignment process.
2D View
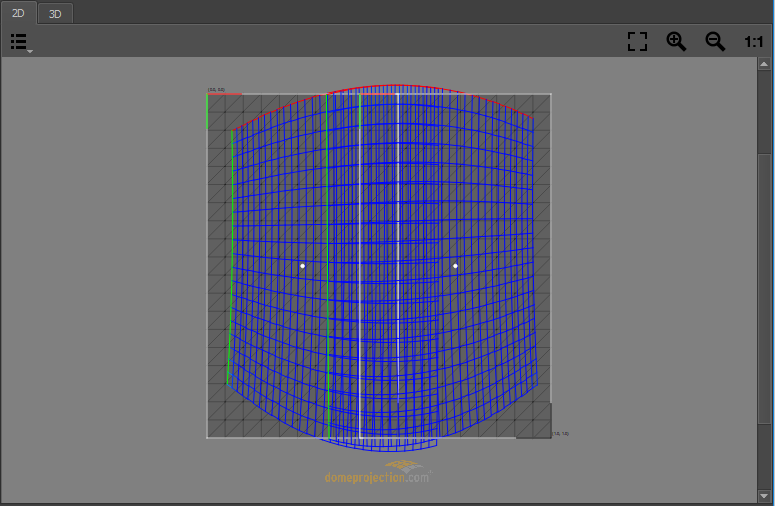
2D View
The 2D View Shows the texture space, a normalized space ranging from (0,0) top-left to (1,1) bottom-right.
Selected projectors are shown in this view as a mesh. The mesh represents the region of the texture used for the corresponding projector. The red and green edge represent the top and left edge of the projector. The mesh is also colored depending on the estimated quality of the calibration. The quality gradient ranges from blue (very good) over green and yellow to red (bad).
- Visualization Options
A drop down menu on the top left corner allows to selet multiple visualization options.
- Cutting Rectangles
The cutting rectangle of the selected projector is shown. The red/green lines mark the top left corner of the cutting rectangle. The black lines mark the bottom right corner. A white dot marks the center of the cutting rectangle.
- Reference Image
The projects reference image set in project settings can be shown as background. It can be set in global project settings, see section General for details.
- Fadeout
In addition a visualization of the fadeout can be activated. The fadeout start and stop edge is marked by a white and black line. The fadeout can be adjusted in mapping settings, see section Shading for further informations.
- UV-Layout
A semi-transparent grid visualizing the area covered by the current mapping. This area is influenced by current mappings uv transform. Especially interesting for “Reference Mesh” mapping. See section Mapping for further information about mappings.
- Navigation
The view can be dragged with the left mouse button.
- Scaling
Several scaling options are available at the top right corner of 2D View.
3D View

3D View
Shows the measured screen and mapping visualization in 3d space. Several aspects of the visualization can be toggled in this views toolbar at the top edge.
- Visualization Options
A drop down menu on the top left corner allows to select multiple visualization options.
- Mapping
Represents the current Mapping-settings. It shows the screen-shape and iconic projection-rays at the corners of the screen. In addition the projection of the measured points onto the screen are visualized.
- Projection
The measured projection can be visualized in three different ways:
- Measured Points
3d-position of measured points.
- Measured Mesh
Triangulation of measured points. If a reference-image is set, the image will be shown as texture on the geometry.
- Full Mesh
Based on current Measurements, the full projector is reconstructed (unmeasured parts as well). If a reference-image is set, the image will be shown as texture on the geometry.
- Perspective
Switch to predefined orthographic views or the default perspective camera position.
- Navigation
Navigate the 3d view using the mouse.
- Rotate
Left mouse-button- Move
Middle mouse-button,Alt+Shift+LMB- Zoom
Right mouse-button,Alt+Ctrl+LMB
Project Settings
The project settings allow to adjust global settings for a project. The
project settings can be found in the Project/Project Settings...
General

General Settings
- Reference Image
An image that will be shown in background of 2d view. Resolution and Aspect-ratio of this image is also shown in the statusbar. So its aspect ratio can be compared with the aspect-ratio of the current mapping-settings.
- Boundingbox Scale
The auto generated cutting rectangles touch the warping mesh by default (scale 1.0). A save area can be added by increasing this value. Typically used when the project will be recalibrated and presplit content is used where the cutting-rectangles must be fixed, other wise the presplit content would have to be recreated.
- Boundingbox Mode
Select if cutting rectangles should be unrotated or rotated. Several exports require the cutting to be unrotated, which is the default.
- Use alignment Data
Used in auto-alignment setups with Align. It switches between the original calibration and the data from recalibration (alignment data)
- Lock Cutting
Avoids accidentally changing cutting-rectangles in projects using presplit content. Cutting-rectangles should be fixed after presplit content is cutted, since it will not fit any more when cutting rectangles are changed.
- Touch Margin
Allows to globally adjust touch margin for touching channels. See section Touching Channels for further information about high resolution projectors with multiple inputs and touching channels.
Interpolation
Captured calibration data is usually incomplete and captured only for a finite number of points. For exporting correction data, Mappers need to interpolate and extrapolate this data for each pixel of a projector and maybe even beyond. Many mathematical strategies exist for that purpose, all with individual strengths and weaknesses.
For some projects, depending on screen and mapping type, it might be
necessary to switch to another interpolation type than the default. This
can be done in the global Settings/Interpolation tab.
Interpolation Settings
Interpolations are used for different purposes in the project.
- General
For all purposes, if not overridden.
- Override 2D
Optional override for interpolations between 2d mapping and projectors (influences the grids seen in 2D view).
- Override full Mesh
Optional override for generating full meshes in 3d (influences full mesh visualization in 3D View and some advanced exporters)
Two interpolation types are available.
- Polynomial (Default)
Gives good generalization of general shape of warping with good exact extrapolation near measured data. Has the tendency to fold and generate wrong results far away from measured data. Has a degree parameter to adjust the complexity of warping. Lower values give better extrapolation results, but less fitting to details and strong curvatures.
- Spline
Gives better results for strong warpings and tight radii, or even sharp corners on screen. Generally captures details better, but has less generalization. More relaxed far distance extrapolation. Takes considerable more time to calculate!
Shading
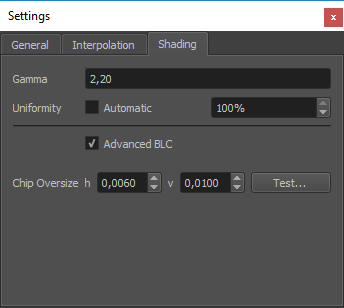
Global shading settings
The shading-tab of the project-settings dialog allows to set several global parameters that influence blending and black-level-adjust calculations.
- Gamma
Gamma of the projectors. Too high values will result in overexposed blending regions, a value that is too low will result in underexposed blending regions.
- Uniformity
Enable automatic global uniformity calculation. Allows to adjust the degree of correction. 100% meaning full uniform brightness as the darkest point in the projection. 50% meaning brightness is reduced for all areas brighter than the medium brightness.
- Advanced BLC
Automatic overlap calculation and regarding uniformity information for black level correction calculations. Brightness and contrast settings for each individual projector are used.
- Max Overlap
Maximum number of projectors overlapping at any point. Typical is 2 for a linear setup of projectors in one row or 4 for a grid of projectors with multiple lines and rows. (Non Advanced BLC only)
- Black level
Projectors typically produce no perfect black. They expose still some light to the screen when the input signal is full black. Black Level describes the amount of light the projector exposes for black images. The corresponding preview can be used to help adjusting this value. (Non Advanced BLC only)
- Chip Oversize
Projectors typically expose light to a larger area than the area of addressable pixels. These surrounding parts must be taken into account for black-level calculation. When they are not regarded, the edges of the overlapping areas will become apparently brighter than the adjacent areas.
- H/V
Horizontal/vertical oversize. Normalized values relative to channel width/height.
- Fade
Compensate for smooth black level spillover typically seen on LCOS projectors. Off by default.
- Test
Project dark triangles on each projector, supposed to line up with the borders of overlapping projectors. The preview regards global chip oversize, as well as potential overrides per channel. If there is a gap between triangles and overlapping projector decrease the chip oversize. If triangles are drawn partly on top of overlapping projectors increase chip oversize.
Preview Toolbar

Preview Toolbar
Several quick previews can be shown on physical screen, to assist during setup of blending, fadeout, ramps, mapping and easy camera.
The most often used previews have a button in the Preview Toolbar. Simply press a preview-button to show or update the corresponding preview.
Under some additional previews can be found.
Please note, that many preview images are results of simplified calculations and therefore not perfect. To judge the quality of a calibration a more time consuming preview export or an export into the real imaging system is needed.
Note
For the preview to work a PatternGenerator must be properly installed and running on each display computer. The warping is handled dynamically by PatternGenerator. Eventually installed warp units should not apply any blending or warping during the preview.
- Black
make all projectors black
- White
make all projectors full white
- Cutting
Visualize, which parts of projectors will be used for projection. Due to intersection of physically projected area and cutting rectangles, this area can be smaller than the actual projector.
- Warping
Visualize the resulting warping grid based on current virtual camera settings.
- Shading
rough shading preview (resolution is depending on projects mesh resolution settings)
- Black Level
rough black level adjust preview (resolution is depending on projects mesh resolution settings)
- Fadeout
rough preview of current fadeout settings (without blending)
- Uniformity
preview of current uniformity correction without blending applied
- Rectangular grid
project a rectangular grid using current mapping settings (typically used with Perspective, Planar, Cylindrical or Spherical LongLat mapping)
- Polar Grid Half Dome
project a circular grid using current mapping settings (typically used for spherical polar mapping)
- Polar Grid Full Dome
project a circular grid using current mapping settings, projects twice as much rings as Half Dome grid. (typically used for spherical polar mapping)
- Outlines
Renders all expected outlines using the calibrated system except for selected projectors. Selected projectors have their current real outline rendered and are filled gray. This can be used to put single projectors easily in their correct position after maintenance and before recalibration. Usage:
Select Projector, that has moved.
Preview Outlines.
Adjust physical projector position, orientation, zoom and shift until it fits its rendered outlines as close as possible.
Re-Align the system to get perfect continuous geometry again.
Statusbar

Mapper2d Status Bar
The statusbar at the bottom of the mainwindow shows multiple status informations.
On the left side it shows event based information.
In the second section it shows the aspect ratio resulting from current mapping settings. The basic mapping settings (min, max values and radius etc. of screen geometry are taken into account). Settings in Transform3d and Transform UV are not taken into account.
In the last section it shows the resolution and aspect-ratio of the current reference image.
Extras
Here additional functionality not yet discussed in other parts of the manual are described. These additional functionalities are usually found in the .
Cut Image
Cut Image is used to cut sub-regions from an image using the current cutting-rectangle. These images can be used as presplit content on the different IGs and warped by warping software/hardware.
Warp Image
Warp Image is used to create preview images for each projector. The warping can be shown, if those images are displayed full-screen on the clients. Select first a source image, which will be used and then the target directory, where the results are stored.
Transform Image
Transform Image currently supports conversion of cube maps into polar images. Additional transformations might be added in future.
Compensate Screen Aspect Ratio
Projection screens are usually not square. They can have rather extreme aspect ratios. Often this is not a problem, since the content is designed for the given screen aspect ratio, and the complete content is just stretched over the screen.
Some playout systems have no idea about of the screen aspect ratio or how the content need to be stretched. They need to get this information from Mappers export, especially the cutting rectangles. In a standard mapper setup the cutting rectangles fill a normalized space, disregarding any screen aspect.
Compensate Screen Aspect Ratio takes the current screen aspect ratio into account and produces texture coordinates and cutting rectangles that appear unstretched.
The aspect ratio can be changed from the default.
Compensate Screen Aspect Ratio settings